The Complete Guide to CBD
What is CBD (cannabidiol)?
CBD (cannabidiol) is a therapeutic compound produced by cannabis. It is commonly extracted and processed into oils, gummies, topicals, and other products that have no doubt sparked your curiosity. And with curiosity comes a load of questions.
This guide is here to lend a hand and provide answers to consumers’ most common questions about CBD, starting with the most basic so you never feel lost. You can start from the beginning or jump straight to whichever CBD question is currently burning hottest for you.
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-intoxicating compound found in cannabis and hemp. CBD oils, gummies, and other products are continuing to grow in popularity as ways to manage anxiety, stress, pain, and other symptoms.
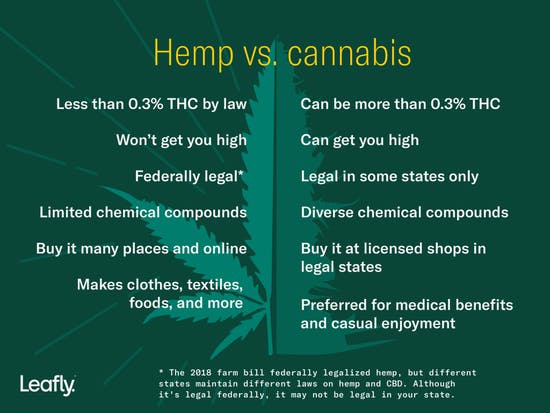
We typically associate cannabis with getting stoned, but CBD can be extracted from the plant to make products that come without the high or the smoke. The molecule in cannabis that gets us high is called THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), and nowadays, you can turn to cannabis-derived CBD products with little to no THC for clear-headed symptom relief.
It’s not just THC and CBD, either—cannabis produces dozens of potentially therapeutic compounds called cannabinoids. We’re slowly getting to know them as legalization spreads, and so far, they seem pretty friendly to us humans and our many ailments.
How does CBD work in the brain and body?
Each of our bodies has a set of receptors that interacts with cannabis compounds called cannabinoids, like CBD. These receptors, found throughout the body, comprise the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex signaling system that ensures our bodies maintain homeostasis.
Put another way, the endocannabinoid system keeps us in balance by directing the communication traffic in our bodies. Cannabinoids such as CBD interact with this system, mimicking natural compounds (called endocannabinoids) produced by the body.
In the human body, CBD influences cannabinoid receptor activity and encourages production of the body’s natural endocannabinoids. Interestingly, CBD also affects activity beyond the endocannabinoid system and can also interact with opioid, dopamine, and serotonin receptors. The ability of CBD to interact with so many different systems throughout the body suggests it has the potential to open new frontiers in psychiatry and medicine.
Can CBD make you feel high?
Unlike THC, CBD is not intoxicating. Why? Both THC and CBD are cannabinoids, but they behave very differently in our bodies.
THC stimulates what are called CB1 receptors. When CB1 receptors are activated, humans generally experience feelings of euphoria—or, for some, anxiety and paranoia. CBD doesn’t activate CB1 receptors, so we don’t feel euphoric, anxious, or stoned when taking it.
In fact, CBD can actually reduce THC’s ability to stimulate CB1 receptors, helping to block some of THC’s not-so-fun side effects. For those prone to anxiety and forgetfulness when consuming cannabis, CBD is a good tool to keep on-hand.